Ever wondered about the
working of a detergent? Detergents makes cleaning easy. Cleaning is rooted in
chemistry. Lets take a look on to the chemistry of detergents.
Classification of dirt
- Organic
- Inorganic
- Combination of organic & inorganic
Organic Soils
This include food soils
such as protein, fat, molds, yeasts etc
and petroleum soils such as grease, motor oil etc. Alkaline cleaners or
solvents can be used to remove organic soils.
Inorganic Soils
This include scales,
rust, hard water deposits and minerals like sand, slit and clay. Acids can be
used to remove inorganic deposits and all-purpose cleaners can be used to
remove minerals.
Combination Soils
This include both
organic and inorganic soils. So it is a challenge to choose the perfect
cleaner. Very concentrated, highly built, solvent containing cleaners are
recommended to clean combination soils.
Detergent composition
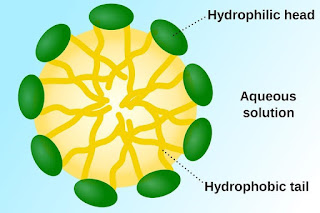
Surfactants
Surface Active Agents
or Surfactants are usually organic compounds that contain both hydrophobic and
hydrophilic groups. Therefore a surfactant contain both water soluble and oil
soluble components. When a surfactant comes in contact with water and dirt, the
hydrophilic heads stays with water and the hydrophobic tail moves away from the
water. The surfactant surrounds the dirt until it is removed.
Chealating Agent
Chelating agent is a
chemical compound and is also known as chelants or sequestering agents. It
reacts with metal ions to form stable and water soluble complexes.
Water hardness is one
of the main problem while cleaning. The presence of iron, calcium, magnesium
and manganese metal ions makes the water harder. These metal ions will use the
surfactants and reduce the ability of detergent in cleaning. Chelating agent
will alter the electronic charge of the metal ions thereby making it impossible
to use the surfactants.
Builders
Builders are often used
as an alternative for chelating agents. It is added to improve the cleaning
efficiency of surfactants. Builders do many functions including softening,
buffering and emulsifying.
Builders soften the
water by deactivating the metal ions present in it. They helps in increasing
the pH and also acts as buffers in maintaining proper alkalinity. Builders helps
in emulsifying by breaking down oily and greasy dirt into tiny particles.
 pH
pH
pH scale ranges from 0
to 14. Anything less than 7 is acid and greater than 7 is base. Any substance
that contain water will have a pH level. pH of a cleaner is important because
it determines how well it works.
Solvents and Preservatives
Water is an active
ingredient in liquid detergents and it adds to the detergency of cleaner. Water
keeps the suspended soil away from the cleaned surface so that it can be carried
away during rinsing. Thus it aids in suspension and prevents in re-deposition
of soils.
Preservatives
are substances that protects the detergents from oxidation, bacterial
degradation, discolouration etc.
*content/pictures used for educational purpose.


Comments
Post a Comment